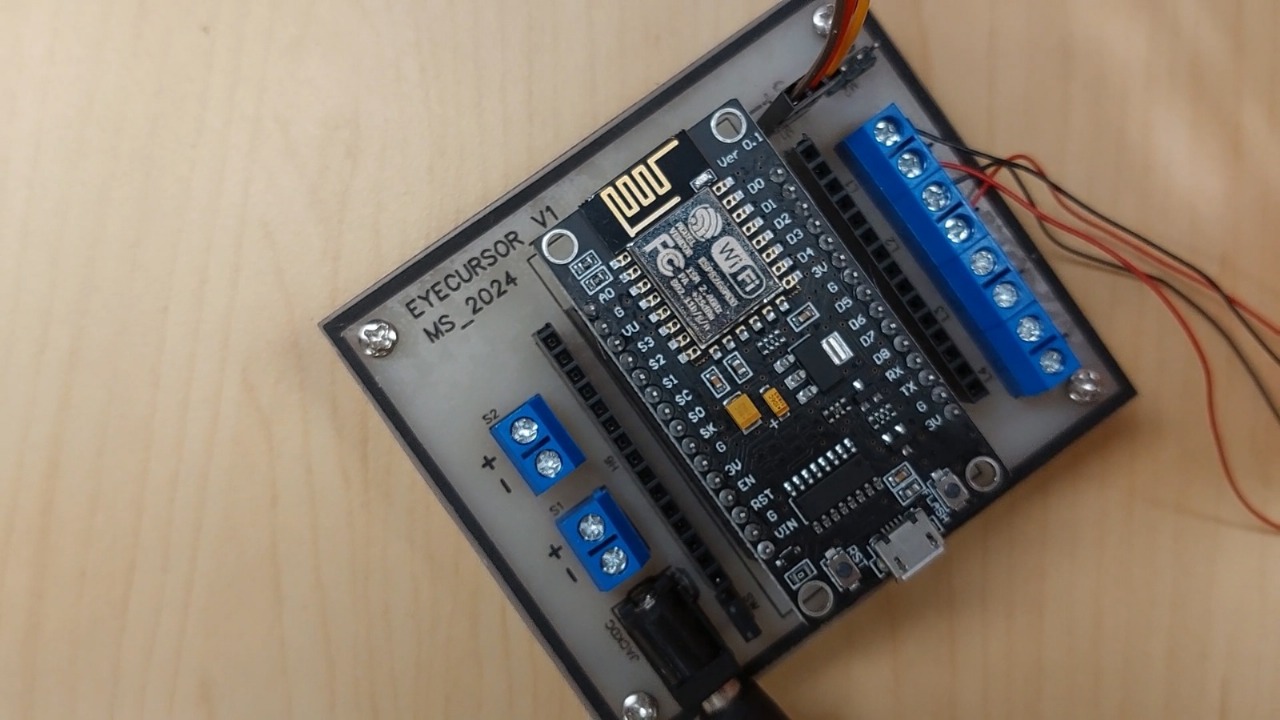
This study assesses a hands-free eye-tracking interaction system developed to empower individuals with physical disabilities and promote inclusive digital access, aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), specifically SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities). Accuracy testing revealed closely grouped gaze points with an estimated precision of 90–95%, while data transmission was highly efficient, averaging just 0.0003 seconds per data point with sustained high throughput. The system consistently delivered a frame rate of approximately 30 FPS, ensuring smooth, real-time performance. Feedback from 10 participants emphasized the system’s ease of use, comfort, responsiveness, and its potential to facilitate independent computer use. High levels of satisfaction reflect the effectiveness of its user-centered design in meeting both technical and practical requirements. By enabling accessible communication and interaction, the system supports digital inclusion for individuals with physical disabilities and contributes to reducing technological barriers. These results underscore its potential as a valuable assistive technology that advances global objectives related to health, well-being, and social equity. In summary, the eye-tracking system offers a practical and inclusive solution that promotes sustainable development by enhancing accessibility and individual empowerment.